Ratify on Alibaba Cloud
This guide will explain how to get up and running with Ratify on Alibaba Cloud using Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) and Alibaba Cloud Container Registry (ACR). This will involve setting up necessary Alibaba Cloud resources, installing necessary components, and configuring them properly. Once everything is set up we will walk through a simple scenario of verifying the signature on a container image at deployment time.
With ACK, you can quickly deploy Gatekeeper and Ratify through visual configuration. With ACR, you can store and distribute images with signatures together. You can use Alibaba Cloud Secrets Manager to keep your signing keys and certificates safe, and then use tools like Notation or Cosign to sign your container images with them.
This article walks you through an end-to-end workflow of deploying only signed images on ACK with Ratify.
Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Prepare the container images in ACR
- Sign ACR images
- Install Ratify & Gatekeeper
- Configure Ratify
- Deploying application in an ACK cluster with a specified image
Prerequisites
-
Already created ACK managed/dedicated cluster, version
1.20or later is required. -
Use Alibaba Cloud ACR to manage container images and signatures.
-
Use Alibaba Cloud KMS service to manage signing keys and certificates.
-
Already install and use Notation CLI plug-in for image signing.
-
Already install notation-alibabacloud-secret-manager plug-in, which could sign the specified image with the keys managed in Alibaba Cloud Secrets Manager based on the plug-in specification of the Notation community.
Prepare the container images in ACR:
- Create an ACR Enterprise Edition instance
- You can use an ACR EE instance to build an image
- The ACR EE instance supports the OCI v1.1.0 Image and Distribution specification, and you can use CLI tools such as ORAS to manage and distribute OCI artifacts such as image signatures and SBOMs, for details, please refer to Using OCI v1.1.0 Specification to Manage and Associate Container Images and Their Derivative Artifacts
- You have configured access control on the proprietary network or public network for connecting to the ACR EE instance, for details, please refer to Configure network access control.
- You have obtained the password for logging to the ACR EE instance. You can reset it if you forget or lose your password, for details, please refer to Configure access credentials for a Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance.
Sign ACR images
Sign with Notation and the keys managed in Alibaba Cloud KMS service
Alibaba Cloud Key Management Service (KMS) is a comprehensive on-cloud data encryption solution that includes KMS and Cloud Hardware Security Module. This solution helps solve concerns such as data security, key security, key management, and secret management. User can sign the specific image with the keys and certificates in Alibaba Cloud Secrets Manager based on the plug-in specification of the Notation community.
Configuration instructions
The notation-alibabacloud-secret-manager plugin uses the KMS Instance SDK and you need to meet the following prerequisites and customize the environment variables:
| Env | Description |
|---|---|
| ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID | Alibaba Cloud Account Access Key ID |
| ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET | Alibaba Cloud Account Secret Access Key |
| ALIBABA_CLOUD_KMS_INSTANCE_ENDPOINT | VPC Endpoint of the Dedicated KMS Instance, for example, kst-hzxxxxxxxxxx.cryptoservice.kms.aliyuncs.com |
| ALIBABA_CLOUD_KMS_CLIENTKEY_FILEPATH | Local File Path of the ClientKey Credential for the Dedicated KMS Instance Application Access Point (AAP) |
| ALIBABA_CLOUD_KMS_PASSWORD | Password for the Dedicated KMS Instance Application Access Point (AAP) |
| ALIBABA_CLOUD_KMS_CA_FILEPATH | Local Path of the CA Certificate for the Dedicated KMS Instance |
Note: The notation-alibabacloud-secret-manager plugin supports multiple credentials configuration methods. Please refer to credentials for more configuration options.
Managing KMS instances
User can enable and manage KMS instances from the console, please refer to the Prerequisites when enabling a KMS instance
The plugin supports signing with two types of keys:
- Keys are created and managed by KMS instances
- Keys are self-signed and imported to KMS instances.
Option 1: Using KMS created and managed keys
Users can create keys in the KMS service console by following these steps.
-
Log in to the Key Management Service Console, and after selecting the target region in the top menu bar, click Resources > Keys in the left navigation bar.
-
On the Keys page, click the Keys tab, and select the target Key Management instance for the Instance ID, and click Create Key.
-
In the Create Key panel, complete the configuration settings, noting that you need to select Asymmetric Key for Key Type, SIGN/VERIFY for Key Usage, and select the Key Specifications supported by Plug-in Specification Compatibility (
RSA-2048,RSA-3072,EC-256) above, and then click OK. -
Execute the following notation CLI signing command to sign the specified image in ACR repository
notation sign --id <keyId> --plugin alibabacloud.secretmanager.plugin $REGISTRY/$REPO:$TAG --plugin-config output_cert_dir=<dirPath>
Option 2: Use self-signed and imported key material
Users can use self-signed keys and import key material into KMS instance management. As a quick start, this tutorial uses openssl to generate private keys and certificates
- Create asymmetric keys in the KMS console, see Step 1.
- Download a wrapping public key and an import token, see Step 2.
- Encrypt the key material with the wrapping public key, see Step 3.
- Import the key material, see Step 4.
Artifact Signing with Notation CLI
Now that we have completed all the configuration, let's start the artifact signing with Notation CLI. If you haven't downloaded the notation CLI tool, you can get it here.
notation sign --id <keyId> --plugin alibabacloud.secretmanager.plugin <myRegistry>/<myRepo>@<digest> --plugin-config output_cert_dir=<dirPath>
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| id | Specificed Alibaba Cloud KMS Instance ID |
| plugin-config | Plugin customized parameters, support the following configurations: output_cert_dir:User can use this parameter to issue the corresponding x509 certificate based on the specified KMS key during the signing process, and output it as a file to the directory specified in this parameter. ca_certs:When signing with the imported self-signed key material, if you also self issued an x509 certificate with the key, you can use the parameter to specify the filepath of the self-signed certificate. |
Install Ratify & Gatekeeper
Prerequisites
- Already created ACK managed/dedicated cluster, version
1.20or later is required. - Gatekeeper-based policy governance is enabled in the cluster, refer to Install or upgrade policy governance components
Install Ratify
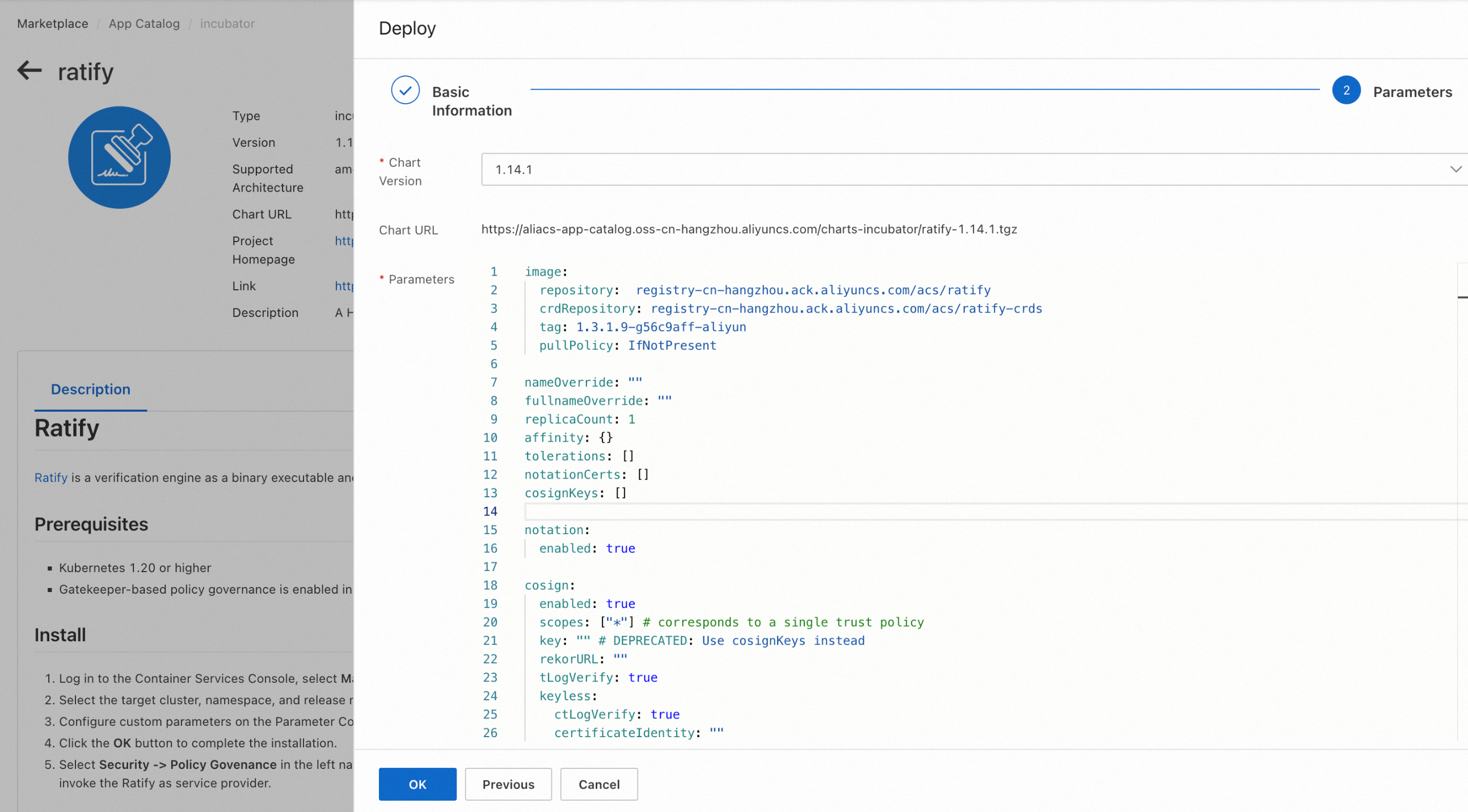
- Log in to the Container Services Console, select Marketplace -> App Catalog in the left navigation bar, enter ratify in the search bar, and click Deploy in the upper right corner of the application page
- Select the target cluster, namespace, and release name for the installation.
- Configure custom parameters on the Parameter Configuration page, the following table lists the common custom configuration options and descriptions when deploying Ratify Helm Chart, note that the notationCerts parameter needs to be set to the list of certificates returned by the KMS service during the previous signing process, for more information about the parameters of Ratify Helm Chart, please refer to the parameter list in the description page of Ratify component in ACK Marketplace.
- Click the OK button to complete the installation.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| notationCerts | An array of public certificate/certificate chain used to create inline certstore used by Notation verifier | `` |
| serviceAccount.create | Create new dedicated Ratify service account | true |
| serviceAccount.name | Name of Ratify service account to create | ratify-admin |
| serviceAccount.annotations | Annotations to add to the service account | {} |
| oras.authProviders.k8secretsEnabled | Enables kubernetes secrets authentication provider for registry interactions | false |
| oras.authProviders.alibabacloudAcrBasicEnabled | Enables Alibaba Cloud ACR basic authentication provider | false |
| oras.cache.enabled | Enables ORAS store cache for ListReferrers and GetSubjectDescriptor. TTL-based cache may cause inconsistency between cache and data source. Please disable it if strong consistency is required.operations | true |
| oras.cache.ttl | Sets the ttl for ORAS store in seconds. cache | 10 |
| alibabacloudAcrConfig.defaultInstanceId | Default instance ID of the Alibaba Cloud Registry where the target artifacts stored | `` |
| alibabacloudAcrConfig.acrInstancesConfig | When images need to be pulled from multiple instances of Aliababa Cloud Registry, the instanceName and instanceId of the instances need to be defined separately in the list, e.g. acrInstancesConfig: - instanceName: name1 instanceId: cri-xxx1 - instanceName: name2 instanceId: cri-xxx2 | [] |
| upgradeCRDs.enabled | Enable/disable Ratify CRD upgrades as pre-install chart hooks | true |
| featureFlags.RATIFY_CERT_ROTATION | Enables/disables tls certificate rotation | false |
| notationCert | DEPRECATED Please switch to notationCerts to specify an array of verification certificates. Public certificate/certificate chain used to create inline certstore used by Notation verifier. |
Deploy RatifyVerification policy instance
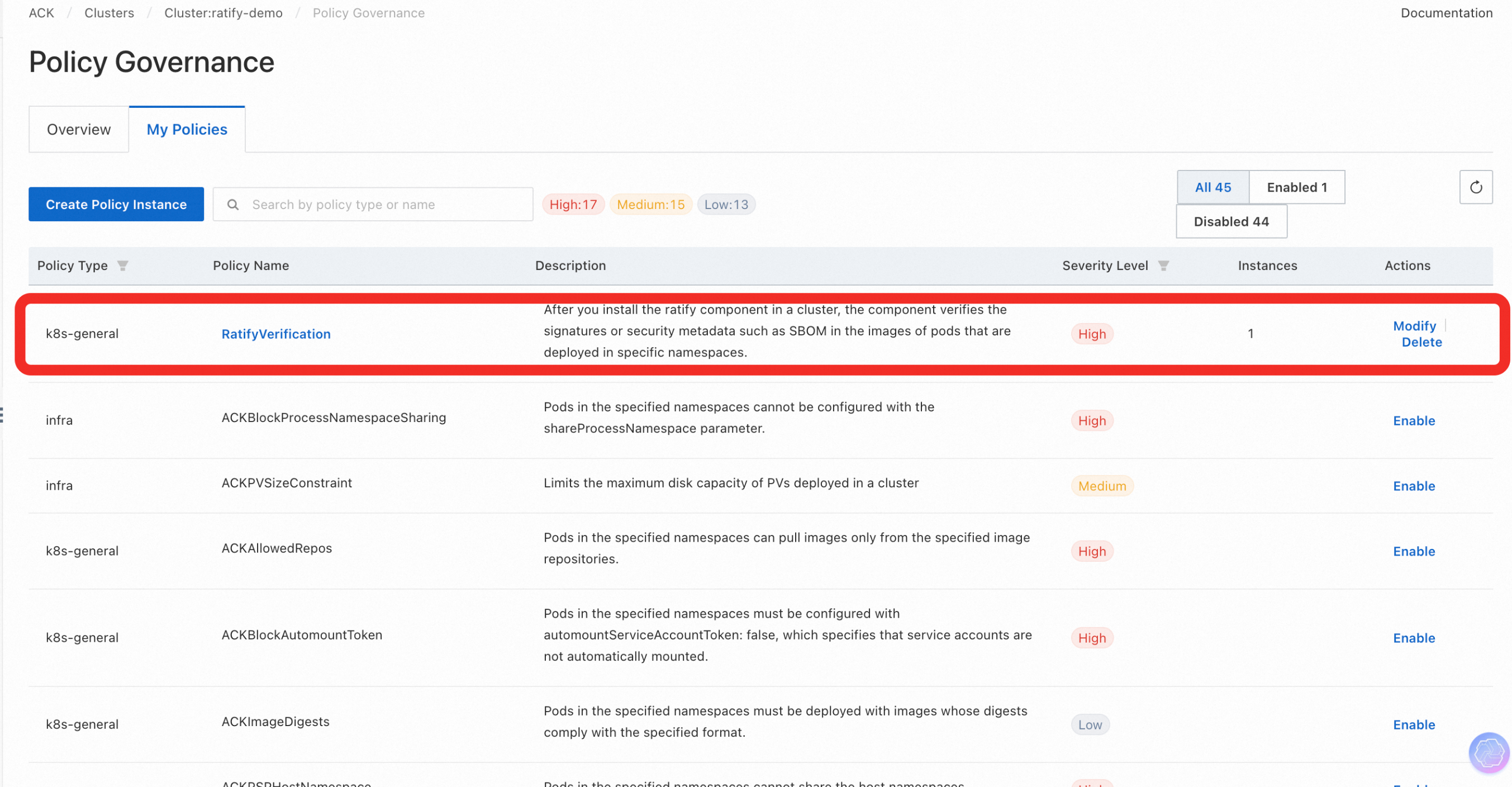
- Select Security -> Policy Governance in the left navigation bar, and refer to the Work with the policy governance feature to deploy the policy RatifyVerification, which is based on Gatekeeper's external data mechanism to invoke the Ratify as service provider.
- Run the following kubectl command to see if the constrainttemplate and constraint instances corresponding to the Gatekeeper policy have been deployed in the cluster, or you can view the current status of the RatifyVerification policy on the Policy Governance page of the console:
kubectl get constrainttemplate ratifyverification
kubectl get constraint | grep ratify-constraint
Configure Ratify
Configuring a verifier to validate artifact's Notation signature
Ratify provides a variety of built-in and external verifier plug-ins. Users must define the name and artifactType fields in the verifier to specify the type of artifact that the verifier will process. verifiers support either cluster-wide resources(using the kind Verifier) or namespaced resources(using the kind NamespacedVerifier). For more information on the verifier, please refer to the official Ratify documentation.
After installing Ratify with the default configuration, the following notation verifier instance will be created in the cluster, and you can configure the specific trustPolicyDoc policy according to the actual usage requirements:
apiVersion: config.ratify.deislabs.io/v1beta1
kind: Verifier
metadata:
name: verifier-notation
spec:
artifactTypes: application/vnd.cncf.notary.signature
name: notation
parameters:
trustPolicyDoc:
trustPolicies:
- name: default
registryScopes:
- '*'
signatureVerification:
level: strict
trustStores:
- ca:certs
trustedIdentities:
- '*'
version: "1.0"
verificationCertStores:
certs:
- ratify-notation-inline-cert
version: 1.0.0
status:
issuccess: true
KeyManagementProvider Configuration
Ratify provides CRD KeyManagementProvider for defining keys or certificates used by verifiers for signature verification in different scenarios. Users can customize the KeyManagementProvider instances according to different signature verification requirements and define the public keys or x.509 certificates in the CR. Notation and Cosign verifiers can consume KeyManagementProvider resources to use during signature verification.
Key Management Provider can be defined as cluster-wide resources(using the kind KeyManagementProvider) or namespaced resources(using the kind NamespacedKeyManagementProvider). For more information about KeyManagementProvider (KMP), please refer to documentation.
apiVersion: config.ratify.deislabs.io/v1beta1
kind: KeyManagementProvider
metadata:
name: ratify-notation-inline-cert
spec:
parameters:
contentType: certificate
value: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
XXXXXX
XXXXXX
XXXXXX
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
type: inline
Pulling ACR private image signature manifest with RRSA
Ratify provides Store for discovering and obtaining metadata of the associated type in the subject field of the OCI v1.1 specification. Users can configure the relevant configurations for connecting to the ACR private repository in the authProvider field of the default oras store instance, where the name field needs to be specified as alibabacloudAcrBasic, acrInstancesConfig field supports configuration of multiple ACR repository instances. Ratify will try to get the repository's corresponding instance ID from the list of mapping relationships defined in acrInstancesConfigaccording to the given workload image name, and if no one found, Ratify will use the instance ID value specified in the defaultInstanceId field and then obtains a temporary username and token for logging in to the ACR repository instance based on the Alibaba Cloud Credentials configured in the environment.
An example configuration is shown below:
apiVersion: config.ratify.deislabs.io/v1beta1
kind: Store
metadata:
name: store-oras
spec:
name: oras
parameters:
authProvider:
acrInstancesConfig:
- instanceName: name1
instanceId: cri-aaaaaaaaaaaa
- instanceName: name2
instanceId: cri-bbbbbbbbbbbb
defaultInstanceId: cri-ccccccccc
name: alibabacloudAcrBasic
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | N | The authProvider name for ACR is fixed to alibabacloudAcrBasic |
| acrInstancesConfig | N | When images need to be pulled from multiple instances of Aliababa Cloud Registry, the instanceName and instanceId of the instances need to be defined separately in the list, e.g. acrInstancesConfig: - instanceName: name1 instanceId: cri-xxx1 - instanceName: name2 instanceId: cri-xxx2 |
| defaultInstanceId | Y | Default instance ID of the Alibaba Cloud Registry where the target artifacts stored |
An example of the parameter configuration snippet that should be configured in Marketplace is shown below:
alibabacloudAcrConfig:
defaultInstanceId: cri-ccccccccc
acrInstancesConfig:
- name1: cri-aaaaaaaaaaaa
- name2: cri-bbbbbbbbbbbb
oras:
useHttp: false
authProviders:
k8secretsEnabled: false
alibabacloudAcrBasicEnabled: true
When using the authProvider of type alibabacloudAcrBasic, Ratify supports pulling signature manifest from the ACR private repository with RRSA (RAM Roles for Service Accounts). The summary of the configuration process is as follows. For more detailed configuration and usage instructions, please refer to Work with RRSA:
- Install the ack-pod-identity-webhook component on the Operations -> Add-ons page of the specified cluster.
- Create the specified RAM role, and modify the trust policy of the RAM role based on the following template, or you can use the ack-ram-tool CLI tool to complete the automated configuration.
{
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"oidc:aud": "sts.aliyuncs.com",
"oidc:iss": "<oidc_issuer_url>",
"oidc:sub": "system:serviceaccount:<namespace>:<service_account>"
}
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": [
"<oidc_provider_arn>"
]
}
}
- Authorize the above RAM roles
- Create a serviceaccount before deploying Ratify, and set the serviceaccount annotations and the namespace labels where Ratify will be deployed:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ratify #Specify the name of the namespace
labels:
pod-identity.alibabacloud.com/injection: 'on'
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: ratify-sa #Specify the name of the serviceaccount
namespace: ratify #Specify the name of the namespace
annotations:
pod-identity.alibabacloud.com/role-name: ratify-role #The RAM Role name created in step 2
---
- After deploying Ratify, you can check whether the Env in the Pod instance template of Ratify has been injected with the specified environment variables:
ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_ARN,ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_PROVIDER_ARNandALIBABABA_CLOUD_OIDC_TOKEN_FILE.
Deploying application in an ACK cluster with a specified image
After completing the above deployment and configuration, try to deploy the application in the cluster. When deploying a signed image, the workload was verified successfully and deployed to the target cluster. When deploying an unsigned image, you can check if Ratify has denied the deployment. You can view the Ratify pod logs for details.
kubectl logs -l app.kubernetes.io/name=ratify --tail=100 -n ratify-service

